We will show thereafter that for a surface of a sphere like the Earth:
- - the part of a meridian joining the equator to the north pole is a geodesic
- - a great circle as the equator is also a geodesic.
- - a line of latitude on the top part of the sphere is not a geodesic
We know from our previous article Geodesic exercise part I: calculation for 2-dimensional Euclidean space that the geodesic equation can be written as
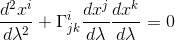
In spherical polar coordinates for a two dimensional surface where r = cste, the index i equals 1 or 2 and x1 = θ, x2 = φ.
We then need the connection coefficients for a surface of a sphere as calculated previously in Christoffel symbol exercise: calculation in polar coordinates part II
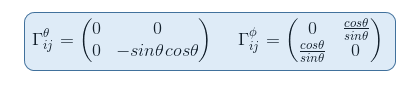
In the geodesic equation, if we replace xi by θ, we have to sum over four elements in the form of Γθjk.
But the only connection coefficient not null in the form of Γθjk is Γθφφ = -sinθ cosθ so that the geodesic equation becomes (i=θ, j=φ, k=φ)
Equation 1
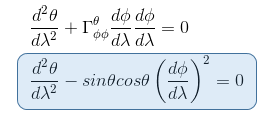
Now we have to replace xi by φ In the geodesic equation, and therefore we have to sum over four elements in the form of Γφjk.
As the only two connection coefficients in the form of Γφjk which are not null are Γφφθ = Γφθφ = cosθ/sinθ then the geodesic equation becomes (i= φ , j=θ, k=φ and i= φ , j=φ, k=θ ) :
Equation 2
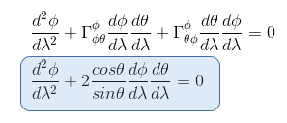
Checking that the meridian is a geodeisc
If we parameterise our meridian by saying that θ = λ where 0 <= λ <= π/2, and φ = 0
then dθ/dλ = 1 => d2θ/dλ2 = 0 also as φ = 0, then dφ/dλ = d2φ/dλ2 = 0
So equation 1 becomes 0 - sinθcosθ x 0 = 0 so 0 = 0 which holds true
In the same way, equation 2 becomes 0 + 2(cosθ/sinθ) x 1 x 0 = 0 <=> 0 = 0 which is verified
Both equations 1 and 2 are true (left-hand side equals the right hand side), therefore they satisfy the geodesic equations, meaning we have shown that the meridian is a geodesic.
Checking that the equator is a geodeisc
If we parameterise our equator by saying that θ = π/2 and φ = λ where 0 <= λ <= 2π
then dφ/dλ = 1 => d2φ/dλ2 = 0 also as θ = π/2, then dθ/dλ = d2θ/dλ2 = 0 and cosθ = cos (π/2) = 0 sinθ = sin(π/2)=1
So equation 1 becomes 0 - 1 x 0 x 12 = 0 so 0 = 0 which holds true
In the same way, equation 2 becomes 0 + 2 x 0 x 0 x 1 = 0 <=> 0 = 0 which is verified
Because equations 1 and 2 are true (left-hand side equals the right hand side), therefore they satisfy the geodesic equations, meaning we have shown that the equator is a geodesic.
Checking that a top latitude line is not a geodeisc
Let's take now the example of a circle on the top part of the sphere defined by θ = π/4 and φ = λ where 0 <= λ <= 2π
Then dφ/dλ = 1 => d2φ/dλ2 = 0 also as θ = π/4, then dθ/dλ = d2θ/dλ2 = 0 and cosθ = cos (π/4) = sinθ = sin(π/4)= √ 2
So equation 1 becomes 0 - √ 2 x √ 2 x 12 = -2 ! = 0 (not true!)
Equation 2 becomes 0 + 2 x 1 x 0 = 0 <=> 0 = 0 which is verified
As equation 1 is not verified even if equation 2 Is verified, it means this top circle of latitude is a not geodesic.